Upwelling in the Banda Sea
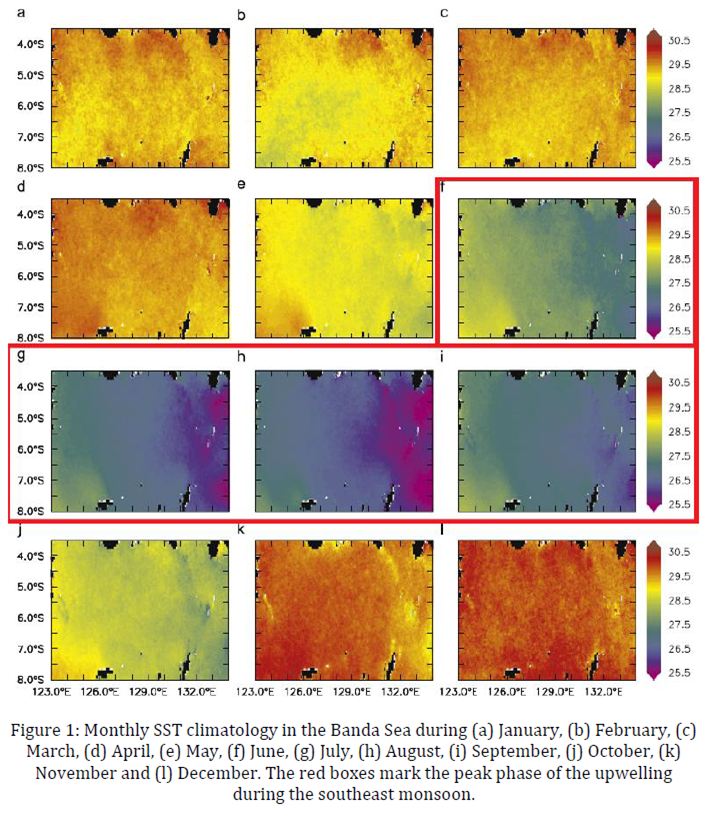
In the southeast monsoon, the sea surface temperature (SST) in the Banda Sea is comparatively lower than in the northwest monsoon. Low SST in the Banda Sea are due to seasonal upwelling during the southeast monsoon (Gordon and Susanto, 2001; Iskandar, 2010; Moore II et al., 2003; Wyrtki, 1961), which peaked between June and September (Gordon and Susanto, 2001; Rachman et al., 2020). There are a variety of views on upwelling driven processes in the Banda Sea. The most common mechanism is suggested by Wyrtki (1961, 1957), who claimed that the upwelling in the Banda Sea is driven by prevailing southeasterly wind during the southeast monsoon. Wyrtki’s concept is further clarified by Longhurst (1993) who indicated that the southeasterly wind during the southeast monsoon generate zonal wind stress, which create offshore Ekman transport, lead to surface divergence in the ocean surface and lead to upwelling in the Banda Sea. Ekman pumping due to the wind stress curl is also referred as an important mechanism in the generation of upwelling in the Banda Sea (Gordon and Susanto, 2001; Iskandar, 2010; Wyrtki, 1958). However, Ratnawati et al. (2016) stated that the Ekman pumping is more important than the Ekman transport to induce upwelling. Upwelling impacts primary productivity in the Banda Sea where it induces a high concentration of chlorophyll (Marpaung et al., 2020; Moore II et al., 2003; Schalk, 1987; Susanto et al., 2006). The upwelling in the Banda Sea is influenced by El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) where during the El Niño, the upwelling is weaker while stronger during La Niña (Gordon and Susanto, 2001).
References
Gordon, A.L., Susanto, R.D., 2001. Banda Sea surface-layer divergence. Ocean Dyn. 52, 2–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-001-8172-6
Iskandar, I., 2010. Seasonal and interannual patterns of sea surface temperature in Banda Sea as revealed by self-organizing map. Cont. Shelf Res. 30, 1136–1148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2010.03.003
Longhurst, A., 1993. Seasonal cooling and blooming in tropical oceans. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 40, 2145–2165. https://doi.org/10.1016/0967-0637(93)90095-K
Marpaung, S., Faristyawan, R., Purwanto, A.D., Asriningrum, W., Suhada, A.G., Prayogo, T., Sitorus, J., 2020. Analysis of water productivity in the Banda Sea based on remote sensing data. Int. J. Remote Sens. Earth Sci. 17, 25. https://doi.org/10.30536/j.ijreses.2020.v17.a3280
Moore II, T.S., Marra, J., Alkatiri, A., 2003. Response of the Banda Sea to the southeast monsoon. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 261, 41–49.
Rachman, H.A., Gaol, J.L., Syamsudin, F., As-syakur, A., 2020. Influence of coastal upwelling on sea surface temperature trends Banda Sea. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 429. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/429/1/012015
Ratnawati, H.I., Hidayat, R., Bey, A., June, T., 2016. Upwelling di Laut Banda dan pesisir selatan Jawa serta hubungannya dengan ENSO dan IOD. Omni-Akuatika 12, 119–130.
Schalk, P.H., 1987. Monsoon-related changes in zooplankton biomass in the eastern Banda Sea and Aru Basin. Biol. Oceanogr. 5, 1–12.
Susanto, R.D., Moore, T.S., Marra, J., 2006. Ocean color variability in the Indonesian Seas during the SeaWiFS era. Geochemistry, Geophys. Geosystems 7. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GC001009
Wyrtki, K., 1961. Physical oceanography of the Southeast Asian waters, in: NAGA Report. University of California, La Jolla, p. 195.
Wyrtki, K., 1958. The water exchange between the Pacific and the Indian Oceans in relation to upwelling process, in: Proceedings of the Ninth Pacific Science Congress. Institute of Marine Research, Djakarta, pp. 61–65.
Wyrtki, K., 1957. Die Zirkulation an der Oberfläche der südostasiatischen Gewässer. Dtsch. Hydrogr. Zeitschrift 10, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02113973
